Assume a bullish view that the current EURUSD forex rate of 1.1 will increase further. Today, there are multiple security types available to profit from this trading strategy:
1) You can buy actual euros (i.e. buying euro currency notes worth 11,000 by paying $10,000).
2) You can take a long position in euro forex futures.
3) You can take a position in euro forex options.
The first option needs substantial capital of $10,000, and safe storage for keeping the 11,000 euro currency notes during the investment period. The second option of euro forex futures offers the benefits of low capital requirement because of margin trading available on futures, but comes with the inherent requirement of daily margin money maintenance. (For more details on futures margin money requirement, see Margin Requirements). The third choice involving Forex options offers the benefit of low capital requirement, but without the overhead of margin requirements like futures.
This article discusses how forex options work, and how to trade forex currency pairs through options (with examples). Other details include a list of most common currency pairs for forex options trading and risk-return profile.
Although multiple exchanges offer forex option trading (such as CME Group, ISE, and Eurex), we take NASDAQ-listed currency option contracts to explain the working examples in this article.
A Quick Primer on Options
Call and put are two basic option types. Each option has a predetermined strike price defined at the time of trade as a part of the option contract. Each option also has a predetermined expiry date, after which it ceases to exist. Depending upon where the forex spot rate ends on the expiry date, the profit/loss for the option traders is determined.
Here is an example with graphical representations.
Assume it is May 2015 and the current EURUSD forex rate is 1.1007. A trader has a bullish view that this rate will go higher in one month (by June 2015). He can buy a EURUSD call option by paying the required option premium (the cost of buying call option).
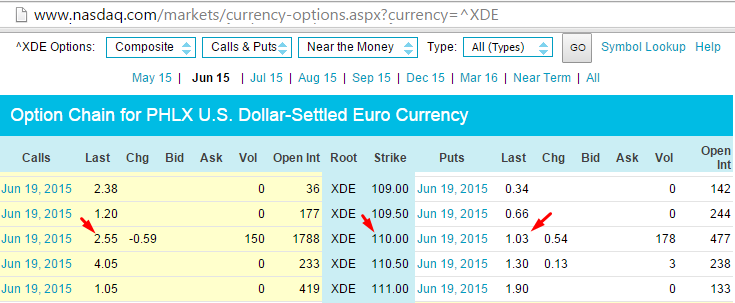
Present-day option price quotes from NASDAQ show that a call option with strike price of 1.10 is available at $2.55.
For
Per NASDAQ forex option specifications, one forex option point is equal to 100 units of the underlying (one point = $100). Thus, a premium quote of $2.55 will cost $255. This is the amount that a forex trader has to pay for buying one contract in EURUSD call options (plus brokerage charges). Also note that due to this convention, the strike price of $1.1 is represented as 110 in the price quote.
Profit and Loss Scenarios for Options Trading
The profit and loss depends on where the EURUSD forex spot rate reaches on the expiry date (June 19, 2015).
Scenario C1: Assume that the EURUSD rate falls below the strike price of 1.10, for example going down to 1.02. The original bullish view of the forex call option buyer did not hold true, and therefore he suffers a loss. He loses the entire option premium ($255) that he paid for buying the call option (plus any brokerage charges).
Scenario C2: Assume that the EURUSD rate goes marginally above the strike price of 1.10, to say 1.15. The buyer of this forex call option is in profit. He benefits on the price differential of (1.15 – 1.10 = 0.05) = 5 points. Multiplying by 100 units per the contract specification gives the total payout as $500. Since he paid $255 upfront as option premium, his profit comes to ($500– $255) = $245 (less any brokerage charges).
Scenario C3: If the EURUSD goes much higher, to say 1.3, the differential from strike price becomes (1.30–1.10) = 0.20 = 20 points, taking the payout to $2,000. Subtracting the paid premium of $255, the profit comes to $1,745.
Effectively, the payout from the forex option contract depends upon the relative difference between strike price and the underlying forex spot prices at the time of expiry. The higher the underlying spot prices (above the strike price), the higher the payout for a call option. Below the strike price, the buyer gets zero payout, leading to loss of premium.
This phenomenon is represented graphically as follows (for a call option):

The RED flat horizontal line represents scenario C1, where the forex spot price ending below the strike price of 1.1 leads to zero payout and thus total loss to the buyer. Scenarios C2 and C3 are represented in the slanted GREEN line, which indicates that higher the underlying forex spot price, the higher the payout. The RED graph (loss zone) and GREEN graph (profit zone) display the complete range of payout for call options.
The forex put works the other way around for the put buyer. You can buy a put if you have a bearish view – for example, EURUSD rates going down from the present day 1.1007 to lower. Currently available at $1.03 premium, the buyer will pay a total of will $103 for one put option contract.
Scenario P1: Assume that the EURUSD rate falls below the strike price of 1.10, for example going down to 1.02. The original bearish view of the forex put option buyer came true, and thus he benefits. The differential (1.10–1.02=0.08) or 8 points provides him a payout of $800. Subtracting the $103 option premium he paid, his profit stands at $697 (less brokerage charges).
Scenario P2: If the EURUSD stays above the strike price of 1.1 at the time of expiry, the put buyer’s view did not come true and he does not get any payout from put option position. He loses his option premium of $103 (plus brokerage charges).
This phenomenon is represented graphically as follows (for a put option):
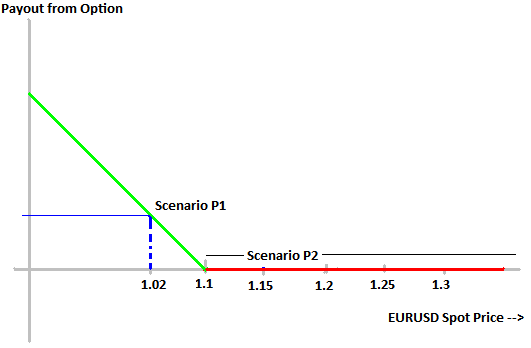
The lower the underlying price goes (below the strike price of 1.1), the more beneficial it is for put option buyer because he receives higher payouts (GREEN graph). The moment the spot price moves above the strike price, there is zero payout from put option and put buyer loses the option premium (RED graph).
Call and put options offer profit payouts in an inverse relationship to underlying forex spot rates. If a buyer believes that the underlying forex rates will increase further by the expiry date, she should buy a call option. The put option is the best choice for the opposite view.
Who’s on the Sell Side?
The above scenarios for call and put are buyer’s positions (long). The sellers will benefit from the opposite price move. In the case of options (or derivatives in general), one man’s gain is other man’s loss.
The call option premium of $255 paid by the buyer is collected by the call option seller. He sells the forex call because he has opposite view – that the EURUSD will remain below 1.10. If his assumption comes true, he gets to keep the entire option premium (scenario C1 above). But if it doesn’t, then he has to pay heavily. The $500 payout in scenario C2 is actually paid by the call option seller to the call option buyer. Similarly, the $2,000 payout in scenario C3 is paid by call option seller to call option buyer.
Similarly, the put option premium of $103 paid by the buyer is collected by the put option seller. He sells the forex put because he believes that the EURUSD will remain higher than 1.10. If his prediction comes true, he gets to keep entire option premium (scenario P2). If otherwise, he pays the buyer (scenario P1).
In essence, the option seller has limited profit potential – capped to the option premium collected. But loss potential is infinite and variable.
Additionally, selling options requires margin money to be maintained, which is another complex requirement on a daily basis. Only experienced option traders with substantial capital should take short sell positions in options. For the novice, the long call and long put positions offer sufficient exposure as needed.
Trading Forex Options
It is not necessary to wait until expiry to benefit from a profitable option position. The option prices (the premium) keep fluctuating every second depending upon a number of factors. (See Option Pricing: Introduction and Option Pricing: Factors That Influence Option Price)
Instead of waiting until expiry, one can simply trade (buy-sell) options and benefit from premium differentials, if bets are placed right.
The Benefits of Forex Options Trading
Long positions in forex options allow low cost exposure. A forex rate change of only 4.55% (from 1.1 to 1.15 in scenario C2) offers profit potential of 96.08% ($500 payout on $255 call trade value) because of the option payoff mechanism. The same 4.55% increase for a physical holding of euro currency notes would have resulted in profits of limited magnitude.
Long positions in options are also better than futures trading. Options magnify the profit exposure with limited capital, but without the mandatory requirement of maintaining daily margin positions, as in futures.
However, the loss potential is also high – losing out all $255 in scenario C1 (or $103 in scenario P1) leads to 100% loss.
The situation is worse if one short sell options – the loss can be much more than the traded amount.
CLICK HERE
Loss Mitigation in Forex Options Trading
There are multiple ways to mitigate the effects of 100% loss in making trades. Instead of holding until expiry, one can actively trade with well-defined profit and stop-loss targets.
The risks can also be mitigated by using efficient capital allocation techniques that structure how much money to bet per trade. For example, properly structured trading plans might enable having four straight loss-making trades in a row, and covering up for them in the fifth trade with overall profit.
The Forex Options Market
The most common and heavily traded currency pairs include the Australian dollar, the British pound, the Canadian dollar, the Euro, the Swiss franc, the New Zealand dollar, and the Japanese yen, all against the US dollar. The same currency pairs have the highest liquidity in the forex options market.
NASDAQ offers forex options trading on seven major currency pairs, enabling trading opportunities to both retail and institutional traders. These include forex options on AUDUSD, GBPUSD, CADUSD, EURUSD, CHFUSD, NZDUSD, and JPYUSD. Traders should note that JPY option contract specification differs slightly from other currency options, owing to its higher currency denomination.
The Bottom Line
The popularity of options trading continues to grow at the individual and institutional levels. The payouts from correctly placed long option forex trades are very high, with the benefit of limited loss potential. However, short option positions should be avoided by novice traders, because they may lead to very high losses, even much larger than the trade value. In-depth study leading to complete familiarity with options pricing and function is mandatory for option trading. Understanding the factors affecting option valuation, followed by thorough practice on free demo-trading accounts, is advisable for option traders, before making big bets in forex options trading ventures.